Download Oracle Essbase 11 Essentials.1z0-531.ExamLabs.2019-03-07.69q.vcex
| Vendor: | Oracle |
| Exam Code: | 1z0-531 |
| Exam Name: | Oracle Essbase 11 Essentials |
| Date: | Mar 07, 2019 |
| File Size: | 2 MB |
How to open VCEX files?
Files with VCEX extension can be opened by ProfExam Simulator.
Discount: 20%
Demo Questions
Question 1
Which six files are involved in database recovery for block storage option after a database crash?
- Essn.pag – data
- Essn.ind – index
- Essn.dat
- Temp.dat
- Dbname.esm - kernel file that contains control information for db recovery
- Dbname.tct - transaction control table
- Dbname.ind - free fragment file for data and index free fragments
- DBname.otl
- Metadata folder
Correct answer: ABEFGH
Explanation:
If there is a problem with any one of these essential database files, the entire database becomes corrupted and Essbase Server cannot start the database:essn.pag (A) essn.ind (B) dbname.esm (E) dbname.tct (F) dbname.ind (G) dbname.otl (for block storage databases) (H): Outline file, which stores all metadata for a database and defines how data is stored, but does not store data itselfTo restore the database, delete these file, restart the database, and reload from data files or from export files backed up before the corruption. Reference: Hyperion, Backup and Recovery GuideUsing Backup and Restore for Block Storage Databases If there is a problem with any one of these essential database files, the entire database becomes
corrupted and Essbase Server cannot start the database:
- essn.pag (A)
- essn.ind (B)
- dbname.esm (E)
- dbname.tct (F)
- dbname.ind (G)
- dbname.otl (for block storage databases) (H): Outline file, which stores all metadata for a database and defines how data is stored, but does not store data itself
To restore the database, delete these file, restart the database, and reload from data files or from export files backed up before the corruption.
Reference: Hyperion, Backup and Recovery Guide
Using Backup and Restore for Block Storage Databases
Question 2
Which two options would provide a better design for the following accounts and metrics?
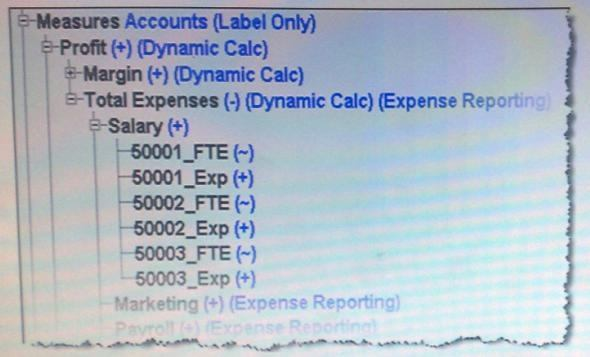
- If there are a small number of accounts that require FTE and Expense dollars, split Accounts and Metrics into 2 dimensions
- If there are a large number of accounts that require FTE and Expense dollars, split Accounts and Metrics into 2 dimensions
- If reporting dictates FTE and dollars in the columns and accounts in the rows, split Accounts and Metrics into 2 dimensions
- If block size is large, then keep Accounts and Metrics as one dimension with a dense dimension
Correct answer: BD
Explanation:
Use Application Design Best Practices, Minimize the number of dimensions, Avoid Repetition in dimensions, Avoid inter dimensional irrelevance. http://www.scribd.com/doc/40391863/10-Hardcore-Essbase-Tuning-Tips-You-Ve-Never-Heard-Before Use Application Design Best Practices, Minimize the number of dimensions, Avoid Repetition in dimensions, Avoid inter dimensional irrelevance.
http://www.scribd.com/doc/40391863/10-Hardcore-Essbase-Tuning-Tips-You-Ve-Never-Heard-Before
Question 3
Identify the two true statements about incremental loading.
- Allows for real time data access for end users.
- Creates *subscribes* along the main slice in the database.
- Materialization of slices is required to provide users the correct query results.
- Different materialized views may exist within a slice as compared to the main slice of the database.
Correct answer: AC
Explanation:
A: Incremental loading and fast aggregation can provide near real-time analysis of transactional data.C: Incremental loading creates subcubes or slices alongside the primary slice of the database.Note: Following a data load, Essbase ASO does not store any aggregate values, but instead calculates them on demand. For large databases, where the time required to generate these values may become inconvenient, the database can materialize one or more aggregate "views", made up of one aggregate level from each dimension (for example, the database may calculate all combinations of the fifth generation of Product with the third generation of Customer), and these views are then used to generate other aggregate values where possible. This process can be partially automated, where the administrator specifies the amount of disk space that may be used, and the database generates views according to actual usage.This approach has a major drawback in that the cube cannot be treated for calculation purposes as a single large hypercube, because aggregate values cannot be directly controlled, so write-back from front-end tools is limited, and complex calculations that cannot be expressed as MDX expressions are not possible. Hyperion Essbase - System 9 Database Administrator's Guide A: Incremental loading and fast aggregation can provide near real-time analysis of transactional data.
C: Incremental loading creates subcubes or slices alongside the primary slice of the database.
Note: Following a data load, Essbase ASO does not store any aggregate values, but instead calculates them on demand. For large databases, where the time required to generate these values may become inconvenient, the database can materialize one or more aggregate "views", made up of one aggregate level from each dimension (for example, the database may calculate all combinations of the fifth generation of Product with the third generation of Customer), and these views are then used to generate other aggregate values where possible. This process can be partially automated, where the administrator specifies the amount of disk space that may be used, and the database generates views according to actual usage.
This approach has a major drawback in that the cube cannot be treated for calculation purposes as a single large hypercube, because aggregate values cannot be directly controlled, so write-back from front-end tools is limited, and complex calculations that cannot be expressed as MDX expressions are not possible.
Hyperion Essbase - System 9 Database Administrator's Guide
Question 4
You should back up the following three for ASO.
- Hyperion_Home \common
- Essbaseinstallfolder\bin
- ARBORPATH \app\appname
- Essbaseinstallfolder \locale
- Essbase.sec
- Essbase.cfg
Correct answer: CEF
Explanation:
C: The application directory should be backup up. BAckups for ASO File system backups are the best method for aggregate storage databases. To backup an ASO database, 9.1. Stop the application. 9.2. Using the File system to back up the arborpath\app\appnameE: essbase.sec* -- Essbase security fileF: essbase.cfg -- Essbase Server configuration fileReference: Roske, Edward; Tracy McMullen (2009-04-30). Look Smarter Than You Are with Essbase 11: An Administrator's Guide (Kindle Locations 8441-8444). interRel Press. Kindle Edition. C: The application directory should be backup up. BAckups for ASO File system backups are the best method for aggregate storage databases. To backup an ASO database, 9.1. Stop the application. 9.2. Using the File system to back up the arborpath\app\appname
E: essbase.sec* -- Essbase security file
F: essbase.cfg -- Essbase Server configuration file
Reference: Roske, Edward; Tracy McMullen (2009-04-30). Look Smarter Than You Are with Essbase 11: An Administrator's Guide (Kindle Locations 8441-8444). interRel Press. Kindle Edition.
Question 5
You have the following analysis requirement. Products roll up to Product Family which rolls up to Product Category. You also need to group Products by Product Manager. Product Managers may manage one or more Products across product families. You do not need to create reports with Product Manager by Product Family. You need to secure products by Product Manager for planning submissions.
You consider Shared members as a solution because of which two options?
- Shared members provide cross tab reporting (Product Manager in the rows and Product Family across the column)
- Shared members provide additional categorization but results in a smaller database then if you were to add Product Manager as a separate dimension
- You can assign security to shared members
- Shared members can be assigned to sparse members only
Correct answer: BC
Explanation:
The data values associated with a shared member come from another member with the same name. The shared member stores a pointer to data contained in the other member, and the data is stored only once. To define a member as shared, an actual nonshared member of the same name must exist. Using shared members lets you use members repeatedly throughout a dimension. Essbase stores the data value only once, but it displays in multiple locations. Storing the data value only once saves space and improves processing efficiency. (B) Shared members must be in the same dimension. Data can be shared by multiple members. Incorrect answers:A: Attributes, not shared members, offers cross-tab, reportingD. Shared member can be assigned to both dense and sparse members. The data values associated with a shared member come from another member with the same name. The shared member stores a pointer to data contained in the other member, and the data is stored only once. To define a member as shared, an actual nonshared member of the same name must exist.
Using shared members lets you use members repeatedly throughout a dimension. Essbase stores the data value only once, but it displays in multiple locations. Storing the data value only once saves space and improves processing efficiency. (B)
Shared members must be in the same dimension. Data can be shared by multiple members.
Incorrect answers:
A: Attributes, not shared members, offers cross-tab, reporting
D. Shared member can be assigned to both dense and sparse members.
Question 6
Identify four disadvantages / considerations when using a transparent partition.
- Old data
- Slow retrievals
- Slow calculations if referencing dynamic calc members in the source
- Outline sync complexities
- Increased network load
- Downtime required to sync data
Correct answer: BCDE
Explanation:
Disadvantages of Transparent Partitions * Outline synchronization is required (D) If you make changes to one outline, the two outlines are no longer synchronized. Although Essbase makes whatever changes it can to replicated and transparent partitions when the outlines are not synchronized, Essbase may not be able to make the data in the data source available in the data target. Essbase tracks changes that you make to block storage outlines and provides tools to keep your block storage outlines synchronized. Note:Essbase does not enable automatic synchronization of aggregate storage outlines. You must manually make the same changes to the source and target outlines. * Transparent partitions increase network activity, because Essbase transfers the data at the data source across the network to the data target. Increased network activity results in slower retrieval times for users. (E) * Because more users are accessing the data source, retrieval time may be slower. (B) * If the data source fails, users at both the data source and the data target are affected. Therefore, the network and data source must be available whenever users at the data source or data target need them. * (C) When you perform a calculation on a transparent partition, Essbase performs the calculation using the current values of the local data and transparent dependents. Essbase does not recalculate the values of transparent dependents, because the outlines for the data source and the data target may be so different that such a calculation is inaccurate. To calculate all partitions, issue a CALC ALL command for each individual partition, and then perform a CALC ALL command at the top level using the new values for each partition. * Formulas assigned to members in the data source may produce calculated results that are inconsistent with formulas or consolidations defined in the data target, and vice versa. Note: Advantages of Transparent PartitionsTransparent partitions can solve many database problems, but transparent partitions are not always the ideal partition type. * You need less disk space, because you are storing the data in one database. * The data accessed from the data target is always the latest version. (not A) * When the user updates the data at the data source, Essbase makes those changes at the data target. * Individual databases are smaller, so they can be calculated more quickly. * The distribution of the data is invisible to the end user and the end user’s tools. * You can load the data from either the data source or data target. * You can enable write-back functionality for aggregate storage databases by creating a transparent partition between an aggregate storage database as the source and a block storage database as the target. Disadvantages of Transparent Partitions
* Outline synchronization is required (D)
If you make changes to one outline, the two outlines are no longer synchronized. Although Essbase makes whatever changes it can to replicated and transparent partitions when the outlines are not synchronized, Essbase may not be able to make the data in the data source available in the data target.
Essbase tracks changes that you make to block storage outlines and provides tools to keep your block storage outlines synchronized.
Note:
Essbase does not enable automatic synchronization of aggregate storage outlines. You must manually make the same changes to the source and target outlines.
* Transparent partitions increase network activity, because Essbase transfers the data at the data source across the network to the data target. Increased network activity results in slower retrieval times for users. (E)
* Because more users are accessing the data source, retrieval time may be slower. (B)
* If the data source fails, users at both the data source and the data target are affected. Therefore, the network and data source must be available whenever users at the data source or data target need them.
* (C) When you perform a calculation on a transparent partition, Essbase performs the calculation using the current values of the local data and transparent dependents. Essbase does not recalculate the values of transparent dependents, because the outlines for the data source and the data target may be so different that such a calculation is inaccurate. To calculate all partitions, issue a CALC ALL command for each individual partition, and then perform a CALC ALL command at the top level using the new values for each partition.
* Formulas assigned to members in the data source may produce calculated results that are inconsistent with formulas or consolidations defined in the data target, and vice versa.
Note: Advantages of Transparent Partitions
Transparent partitions can solve many database problems, but transparent partitions are not always the ideal partition type.
* You need less disk space, because you are storing the data in one database.
* The data accessed from the data target is always the latest version. (not A)
* When the user updates the data at the data source, Essbase makes those changes at the data target.
* Individual databases are smaller, so they can be calculated more quickly.
* The distribution of the data is invisible to the end user and the end user’s tools.
* You can load the data from either the data source or data target.
* You can enable write-back functionality for aggregate storage databases by creating a transparent partition between an aggregate storage database as the source and a block storage database as the target.
Question 7
Assuming Sales and Year are sparse and Actual is dense, what two actions will the following calc script perform?
FIX (Actual, @CY, Sales)
DATAEXPORT "BINFILE" "data.txt";
ENDFIX
- Export the data for actual, current year, sales into a text file called data.txt
- Export the data for actual, current year into a text file called data.txt
- Export data blocks in a compressed encrypted format
- Create a text file that can be imported using the DATAIMPORTBIN calc command in another database that has different dimensionality
Correct answer: AC
Explanation:
The FIX…ENDFIX command block restricts database calculations to a subset of the database. All commands nested between the FIX and ENDFIX statements are restricted to the specified database subset. Syntax:FIX (fixMbrs) COMMANDS ; ENDFIX fixMbrs: A member name or list of members from any number of database dimensions.DATAEXPORT writes data to a text file, binary file, or as direct input to a relational file using ODBC. The data blocks will be saved in a compressed encrypted format to a text file. For a binary output file:DATAEXPORT "Binfile" "fileName" Incorrect answers:The Sales dimension is included as well. Use the DATAIMPORTBIN command to import a previously exported binary export file. However, the data cannot be imported into another database with a different dimensionality. The FIX…ENDFIX command block restricts database calculations to a subset of the database. All commands nested between the FIX and ENDFIX statements are restricted to the specified database subset.
Syntax:
FIX (fixMbrs)
COMMANDS ;
ENDFIX
fixMbrs: A member name or list of members from any number of database dimensions.
DATAEXPORT writes data to a text file, binary file, or as direct input to a relational file using ODBC. The data blocks will be saved in a compressed encrypted format to a text file.
For a binary output file:
DATAEXPORT "Binfile" "fileName"
Incorrect answers:
- The Sales dimension is included as well.
- Use the DATAIMPORTBIN command to import a previously exported binary export file.
However, the data cannot be imported into another database with a different dimensionality.
Question 8
A calculation script is performed on a database for which Create Block on Equation is OFF. The command SET CREATEBLOCKONEQ ON is issued immediately before an equation in the script.
Which statement accurately describe when blocks will be created?
- Blocks will be created ONLY when the equation assigns non-constant values to members of a sparse dimension
- Blocks will be created ONLY when the equation assigns constant values to members of a sparse dimension
- Blocks will be created when the equation assigns either constant or non-constant values to members of a sparse dimension.
- No blocks will be created.
Correct answer: C
Explanation:
C: Blocks are always (whether or not CREATEBLOCKONEQ is ON or OFF) created when a constant value is assigned to a member of a sparse dimension (for which a block does not exist). When SET CREATEBLOCKONEQ ON blocks will also be created when an non-constant value is assigned to a member of a sparse dimension (for which a block does not exist) in a new block.Note: If this would be a select two alternative question, the alternatives would have to be reworded slightly differently.Note #1:The SET CREATEBLOCKONEQ command controls, within a calculation script, whether or not new blocks are created when a calculation formula assigns anything other than a constant to a member of a sparse dimension. SET CREATEBLOCKONEQ overrides the Create Block on Equation setting for the database. Syntax: SET CREATEBLOCKONEQ ON|OFF;ON: When a calculation formula assigns a non-constant value to a member of a sparse dimension for which a block does not exist, Analytic Services creates a new block.Note #2: The Create Blocks on Equation setting is a database property. The initial value for the Create Blocks on Equation setting is OFF; no new blocks are created when something other than a constant is assigned to a sparse dimension member. You can use Administration Services or MaxL to set the Create Blocks on Equation setting to ON at the database-level. For more information about enabling the Create Blocks on Equation property for a database, see MaxL documentation in the Technical Reference or Administration Services online help.For more specific control, you can use the SET CREATEBLOCKONEQ calculation command within a calculation script to control creation of new blocks at the time the command is encountered in the script. Use of the SET CREATEBLOCKONEQ calculation command has the following characteristics:* When Analytic Services encounters a SET CREATEBLOCKONEQ command within a calculation script, Analytic Services ignores the database-level setting. * Where needed in the calculation script, you can use multiple SET CREATEBLOCKONEQ commands to define the Create Blocks on Equation setting value for the calculations that follow each command. * The value set by the SET CREATEBLOCKONEQ command stays in affect until the next SET CREATEBLOCKONEQ command is processed or the calculation script is finished. Reference: SET CREATEBLOCKONEQ C: Blocks are always (whether or not CREATEBLOCKONEQ is ON or OFF) created when a constant value is assigned to a member of a sparse dimension (for which a block does not exist). When SET CREATEBLOCKONEQ ON blocks will also be created when an non-constant value is assigned to a member of a sparse dimension (for which a block does not exist) in a new block.
Note: If this would be a select two alternative question, the alternatives would have to be reworded slightly differently.
Note #1:
The SET CREATEBLOCKONEQ command controls, within a calculation script, whether or not new blocks are created when a calculation formula assigns anything other than a constant to a member of a sparse dimension. SET CREATEBLOCKONEQ overrides the Create Block on Equation setting for the database.
Syntax: SET CREATEBLOCKONEQ ON|OFF;
ON: When a calculation formula assigns a non-constant value to a member of a sparse dimension for which a block does not exist, Analytic Services creates a new block.
Note #2: The Create Blocks on Equation setting is a database property. The initial value for the Create Blocks on Equation setting is OFF; no new blocks are created when something other than a constant is assigned to a sparse dimension member. You can use Administration Services or MaxL to set the Create Blocks on Equation setting to ON at the database-level. For more information about enabling the Create Blocks on Equation property for a database, see MaxL documentation in the Technical Reference or Administration Services online help.
For more specific control, you can use the SET CREATEBLOCKONEQ calculation command within a calculation script to control creation of new blocks at the time the command is encountered in the script. Use of the SET CREATEBLOCKONEQ calculation command has the following characteristics:
* When Analytic Services encounters a SET CREATEBLOCKONEQ command within a calculation script, Analytic Services ignores the database-level setting.
* Where needed in the calculation script, you can use multiple SET CREATEBLOCKONEQ commands to define the Create Blocks on Equation setting value for the calculations that follow each command.
* The value set by the SET CREATEBLOCKONEQ command stays in affect until the next SET CREATEBLOCKONEQ command is processed or the calculation script is finished.
Reference: SET CREATEBLOCKONEQ
Question 9
Market size is an attribute dimension with the following members: Large, Medium, and Small.
Which of the following options below represent valid syntax statements in a calc script?
- FIX (@ATTRIBUTE(Large))
- Calc Dim (Accounts, Markets, "Market Size");
- Calc Dim (Accounts, Markets, Market Size);
- FIX(Large)
Correct answer: AB
Explanation:
For example, using Sample Basic, assume this statement is in a calculation script:.. FIX (@children(january)) CALC DIM (Accounts, Product, Market) ENDFIX For example, using Sample Basic, assume this statement is in a calculation script:
.. FIX (@children(january))
CALC DIM (Accounts, Product, Market)
ENDFIX

Question 10
Moving a stored entity member in a sparse dimension causes_________.
- a Full restructure
- an Index restructure
- an Outline restructure
- No restructure
Correct answer: B
Explanation:
If a member of a sparse dimension is moved, deleted, or added, Essbase restructures the index and creates new index files. Restructuring the index is relatively fast; the time required depends on the index size. If a member of a sparse dimension is moved, deleted, or added, Essbase restructures the index and creates new index files. Restructuring the index is relatively fast; the time required depends on the index size.
HOW TO OPEN VCE FILES
Use VCE Exam Simulator to open VCE files

HOW TO OPEN VCEX AND EXAM FILES
Use ProfExam Simulator to open VCEX and EXAM files


ProfExam at a 20% markdown
You have the opportunity to purchase ProfExam at a 20% reduced price
Get Now!



