Download Deploying HP FlexNetwork Core Technologies.HP0-Y47.PracticeTest.2018-08-16.28q.vcex
| Vendor: | HP |
| Exam Code: | HP0-Y47 |
| Exam Name: | Deploying HP FlexNetwork Core Technologies |
| Date: | Aug 16, 2018 |
| File Size: | 7 MB |
How to open VCEX files?
Files with VCEX extension can be opened by ProfExam Simulator.
Discount: 20%
Demo Questions
Question 1
How does virtual output queuing (VoQ) help switches avoid head-of-line blocking and enhance throughput?
- It divides each port ingress queue into different queues based on the priority and egress port of each packet
- It establishes a matrix of connections to multiple cross-bar switches within the switch backplane
- It considers traffic congestion, queues traffic, and informs the ingress port when it can use the crossbar
- It allows the ingress port to fragment packets and send the fragments in multiple queues over different crossbars
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
A Virtual Output Queue (VOQ) is the technique used in input-queued switches where rather than keeping all traffic in a single queue, separate queues are maintained for each possible output location. It addresses a common problem known as head-of-line blocking. In VOQ each input port maintains a separate queue for each output port. It has been shown that VOQ can achieve 100% throughput performance with an effective scheduling algorithm. This scheduling algorithm should be able to provide a high speed mapping of packets from inputs to outputs on a cycle-to-cycle basis Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Virtual_Output_Queues A Virtual Output Queue (VOQ) is the technique used in input-queued switches where rather than keeping all traffic in a single queue, separate queues are maintained for each possible output location. It addresses a common problem known as head-of-line blocking.
In VOQ each input port maintains a separate queue for each output port. It has been shown that VOQ can achieve 100% throughput performance with an effective scheduling algorithm. This scheduling algorithm should be able to provide a high speed mapping of packets from inputs to outputs on a cycle-to-cycle basis
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Virtual_Output_Queues
Question 2
A company uses 802.1X authentication to force users to authenticate to connect to the network. The company uses HP IMC User Access manager (UAM) as the RADIUS server. The company wants to assign users to VLANs based on their identity. For example, contractor should be assigned in VLAN 20. Assume that VLANs are extended correctly across the network infrastructure.
Where does a network administrator configure the VLAN policy?
- In the access device configuration UAM
- In local-user accounts for contractors, which are configured on access layer switches
- In an authorized VLAN list, which is applied to access layer switches edge ports
- In an access rule on UAM, which will be selected in the contractor service policy
Correct answer: D
Explanation:
The HP IMC User Access Management (UAM) Module supports user identity authentication based on access policies associated with infrastructure resources. Reference: Intelligent Management Center User Access Management Softwarehttp://h17007.www1.hp.com/us/en/networking/products/network-management/IMC_UAM_Software/index.aspx#.VYeq3vmqpBc The HP IMC User Access Management (UAM) Module supports user identity authentication based on access policies associated with infrastructure resources.
Reference: Intelligent Management Center User Access Management Software
http://h17007.www1.hp.com/us/en/networking/products/network-management/IMC_UAM_Software/index.aspx#.VYeq3vmqpBc
Question 3
Refer to the exhibit.
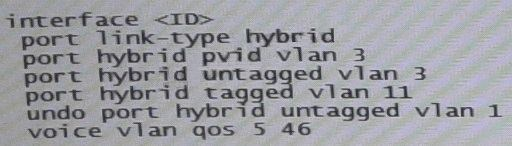
An HP Comware Switch connects to Voice over (VoIP) phones. The phones connect to user’s computes, so each switch port connects a computer and a phone.
These are the specifications:
- The VLAN for data traffic is VLAN3
- The VLAN for traffic VoIP is VLAN11
- The phones support Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) Media Endpoint Detection (MED).
The network administrator wants to use LLDP-MED to advertise the voice VLAN ID and priority settings to the phones. The phones will then send tagged traffic in that VLAN. The switch should not check the incoming traffic’s MAC address against its voice OID list. The exhibit shows the applicable switch port configuration.
Which additional step must the administrator complete to accomplish this?
- Enable voice VLAN 11 (voice vlan 11 enable)
- Change the port to trunk mode (port link-type trunk)
- Enable LLDP compatibility with Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) (lldp compliance admin-status cdp txrx)
- Enable the port to advertise voice VLAN 11 with LLDP (lldp voice-vlan 11)
Correct answer: D
Explanation:
LLDP must be enabled on this Ethernet ports and are configured to advertise the voice VLAN ID and QoS information using the Network Policy LLDP TLV. Reference: Application Notesfor using Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) with HP ProCurve Switches and Avaya IP Telephones - Issue 1.0http://h17007.www1.hp.com/docs/interoperability/Avaya/ProCurve-lldp.pdf LLDP must be enabled on this Ethernet ports and are configured to advertise the voice VLAN ID and QoS information using the Network Policy LLDP TLV.
Reference: Application Notesfor using Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) with HP ProCurve Switches and Avaya IP Telephones - Issue 1.0
http://h17007.www1.hp.com/docs/interoperability/Avaya/ProCurve-lldp.pdf
Question 4
Refer to the exhibit.
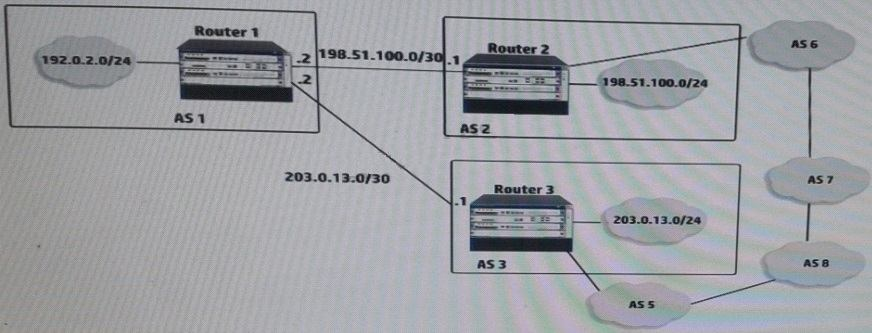
These three routers are currently configured for BGP. They do not apply any routing policy in terms of BGP on routes or attributes advertised to an received from peers. How can the network administrator for Router 1 cause Router 1 to advertise 192.0.2.0/24 to Router 2 and Router 3?
- Enable BGP routing on RAGG1
- Add a null route to 192.0.2.0/24
- Apply route policy 1 as an inbound policy for both peers
- Apply route policy 1 as an outbound policy for both peers
Correct answer: D
Explanation:
You can associate a route policy to a BGP peer. Route policies use route maps to control or modify the routes that BGP recognizes. You can configure a route policy for inbound or outbound route updates. Incorrect:Not B: Null 0 routing is used to prevent routing loops in some conditions as if any packet is destinated for some specific route in that subnet which is not available for an example is down due to any reason instead of going through the default route and packet reaching somewhere else packet destined for that specific route within that subnet must be dropped.So basically NULL 0 creates a block hole where if packets are matched is dropped. Reference: Configuring Advanced BGPhttp://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/datacenter/sw/5_x/nx-os/unicast/configuration/guide/l3_cli_nxos/l3_advbgp.html You can associate a route policy to a BGP peer. Route policies use route maps to control or modify the routes that BGP recognizes. You can configure a route policy for inbound or outbound route updates.
Incorrect:
Not B: Null 0 routing is used to prevent routing loops in some conditions as if any packet is destinated for some specific route in that subnet which is not available for an example is down due to any reason instead of going through the default route and packet reaching somewhere else packet destined for that specific route within that subnet must be dropped.
So basically NULL 0 creates a block hole where if packets are matched is dropped.
Reference: Configuring Advanced BGP
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/datacenter/sw/5_x/nx-os/unicast/configuration/guide/l3_cli_nxos/l3_advbgp.html
Question 5
A company needs a simple authenticate solution for guests. The HP Comware access layer switches will implement portal authentication (or Web-Auth). The network administrator wants the switch to host the login web page on an IP address that not used for any other purpose.
What should the administrator do to accomplish this goal?
- Set the IP address when defining the local portal server, and create a loopback interface for the address
- Create RADIUS scheme that specifies this IP address for the authentication server. Select this scheme for portal authentication in the default domain
- Create a layer 3 interface for the guest VLAN and assign the desired IP address. Activate local portal authentication on this interface.
- Set the IP address when defining the local portal server, and the switch automatically begins using that address.
Correct answer: C
Explanation:
* Enable portal server on Onboarding VLAN Interface, this will activate the default Portal ACL (deny all, redirect tcp port 80 to TCP-Cheat) [comware5]interface Vlan-interface 21 [comware5-Vlan-interface21]portal server uam method layer3 [comware5-Vlan-interface21]quit [comware5] * how the Portal redirect works. These are the basic steps:Admin enables Portal authentication on the Onboarding VLAN L3 Interface, this will effectively block all traffic (default portal ACL) User connects and “should” get an address through DHCP/DHCP Relay. User opens browser, tries to access http://www.hp.comUser Device will send dns request for http://www.hp.com (to DNS IP Provided by DHCP server)DNS “should” respond with public IP of http://www.hp.com (default Portal ACL will block this by default!)Reference: Comware Portal Redirect for BYOD usehttp://abouthpnetworking.com/2014/01/30/comware-portal-redirect-for-byod-use/ * Enable portal server on Onboarding VLAN Interface, this will activate the default Portal ACL (deny all, redirect tcp port 80 to TCP-Cheat)
[comware5]interface Vlan-interface 21
[comware5-Vlan-interface21]portal server uam method layer3
[comware5-Vlan-interface21]quit
[comware5]
* how the Portal redirect works. These are the basic steps:
- Admin enables Portal authentication on the Onboarding VLAN L3 Interface, this will effectively block all traffic (default portal ACL)
- User connects and “should” get an address through DHCP/DHCP Relay.
- User opens browser, tries to access http://www.hp.com
- User Device will send dns request for http://www.hp.com (to DNS IP Provided by DHCP server)
- DNS “should” respond with public IP of http://www.hp.com (default Portal ACL will block this by default!)
Reference: Comware Portal Redirect for BYOD use
http://abouthpnetworking.com/2014/01/30/comware-portal-redirect-for-byod-use/
Question 6
Refer to the exhibit.

A network administrator up a remote mirroring on the HP Comware switches in the exhibit. The administrator must define several port while entering mirroring-group commands on these switches. Which port should be the reflector port (sometimes called monitor-egress port)?
- Switch 1, G1/0/2
- Switch3, T1/0/4
- Switch 1, T1/0/25
- Switch 1, G1/0/1
Correct answer: B
Explanation:
Put it in on the switch that receives remote mirrored traffic. Reference: HP Networking and Cisco CLI Reference Guidehttp://h17007.www1.hp.com/docs/interoperability/Cisco/HP-Networking-and-Cisco-CLI-Reference-Guide_June_10_WW_Eng_ltr.pdf Put it in on the switch that receives remote mirrored traffic.
Reference: HP Networking and Cisco CLI Reference Guide
http://h17007.www1.hp.com/docs/interoperability/Cisco/HP-Networking-and-Cisco-CLI-Reference-Guide_June_10_WW_Eng_ltr.pdf
Question 7
Two HP 10500 Series Switches connect on a 10G fiber link. One of the two fibers in the link breaks, and a broadcast storm occurs.
How could a network administrator prevent a problem like this from happening again?
- Configure Device Link Detection Protocol (DLDP) on both sides of the link.
- Use Rapid Per VLAN Spanning Tree Plus (RPVST+) instead of Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP).
- Implement sFlow or NetStream on both sides of the link, setting the collector to an Intelligent Management Center (IMC) server.
- Add another 10G link and create a link aggregation group on each switch that includes both links.
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
* The Device Link Detection Protocol (DLDP) can detect the link status of a fiber cable or twisted pair. Upon detecting a unidirectional link, DLDP shuts down the faulty port automatically or prompts the user to do so manually depending on the configuration to avoid forwarding problems. * As a link layer protocol, DLDP can identify remote devices, detect unidirectional links, and shut down unreachable ports at the link layer. / If both ends of a link are operating normally at the physical layer, DLDP detects whether the link is correctly connected at the link layer and whether the two ends can exchange packets properly. This is beyond the capability of the auto-negotiation mechanism at the physical layer. / In conjunction with the physical layer auto-negotiation mechanism where physical signals and faults can be detected, DLDP can detect and shut down physically/logically unidirectional links. 2 DLDP Implementation Reference: DLDP Technology White Paperhttp://www.h3c.com/portal/Products___Solutions/Technology/LAN/Technology_White_Paper/200812/623012_57_0.htm * The Device Link Detection Protocol (DLDP) can detect the link status of a fiber cable or twisted pair. Upon detecting a unidirectional link, DLDP shuts down the faulty port automatically or prompts the user to do so manually depending on the configuration to avoid forwarding problems.
* As a link layer protocol, DLDP can identify remote devices, detect unidirectional links, and shut down unreachable ports at the link layer.
/ If both ends of a link are operating normally at the physical layer, DLDP detects whether the link is correctly connected at the link layer and whether the two ends can exchange packets properly. This is beyond the capability of the auto-negotiation mechanism at the physical layer.
/ In conjunction with the physical layer auto-negotiation mechanism where physical signals and faults can be detected, DLDP can detect and shut down physically/logically unidirectional links.
2 DLDP Implementation
Reference: DLDP Technology White Paper
http://www.h3c.com/portal/Products___Solutions/Technology/LAN/Technology_White_Paper/200812/623012_57_0.htm
Question 8
HP Comware Switch 1 connects to switch 2 on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1. Switch 2 implements an inbound rate limit of 600 Mbps. The network administrator wants switch 1 to buffer traffic that exceeds the Switch 2 rate limit of 600 Mbps and send the traffic at 600 Mbps. All traffic has the same 802.1p priority and is forwarded in priority queue 2.
What should the administrator apply to the Switch 1 interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1?
- A line rate limit of 600 Mbps on queue 2
- A QoS policy with a classifier that matches all traffic and a CAR behavior that sets a CIR of 600 Mbps
- A weighted random early discard (WRED) table with a limit of 600 for queue 2
- A traffic shaping rate limit of 600 Mbps on queue 2
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
The line rate of a physical interface specifies the maximum rate of incoming packets or outgoing packets. Note: Configuring the line ratePerform the following steps:Enter system view by using the following command:system-view Enter interface view. interface interface-type interface-number Configure the line rate for the interface. Use the following command:qos lr outbound cir committed-informationrate [ cbs committed-burst-size [ ebs excessburst- size ] ] Reference: HP 6600 Router Series - Configuring Traffic Policing/Traffic Shaping/Line Ratehttp://h20564.www2.hp.com/hpsc/doc/public/display?docId=emr_na-c03146192&sp4ts.oid=5179297#N101D6 The line rate of a physical interface specifies the maximum rate of incoming packets or outgoing packets.
Note: Configuring the line rate
Perform the following steps:
- Enter system view by using the following command:system-view
- Enter interface view.interface interface-type interface-number
- Configure the line rate for the interface. Use the following command:
qos lr outbound cir committed-informationrate [ cbs committed-burst-size [ ebs excessburst- size ] ]
Reference: HP 6600 Router Series - Configuring Traffic Policing/Traffic Shaping/Line Rate
http://h20564.www2.hp.com/hpsc/doc/public/display?docId=emr_na-c03146192&sp4ts.oid=5179297#N101D6
Question 9
What distinguishes an HP switch with a CLOS fabric from an HP switch with a crossbar fabric?
- The CLOS fabric can integrate with a virtual switch, which is deployed in a virtualized server.
- The CLOS fabric is a requirement for an Intelligent Resilient Framework (IRF) virtual switch with more than two members.
- The CLOS fabric can dynamically shut down power to unused switch ports, proving better energy efficiency.
- The CLOS fabric can dynamically load-balance internal traffic over many paths, helping the switch support 40G/100G.
Correct answer: D
Explanation:
In a modern Clos topology, every lower-tier switch is connected to each of the top-tier switches in a full-mesh topology. If there isn't any oversubscription taking place between the lower-tier switches and their uplinks, then a non-blocking architecture can be achieved. The advantage of the Clos network is you can use a set of identical and inexpensive devices to create the tree and gain high performance and resilience that would otherwise cost must more to construct. To prevent any one uplink path from being chosen, the path is randomly chosen so that the traffic load is evenly distributed between the top-tier switches. If one of the top tier switches were to fail, it only slightly degrades performance through the data center. Reference: Clos Networks: What's Old Is New Again, What goes around, comes around – Clos Networks are backhttp://www.networkworld.com/article/2226122/cisco-subnet/clos-networks--what-s-old-is-new-again.html In a modern Clos topology, every lower-tier switch is connected to each of the top-tier switches in a full-mesh topology. If there isn't any oversubscription taking place between the lower-tier switches and their uplinks, then a non-blocking architecture can be achieved. The advantage of the Clos network is you can use a set of identical and inexpensive devices to create the tree and gain high performance and resilience that would otherwise cost must more to construct. To prevent any one uplink path from being chosen, the path is randomly chosen so that the traffic load is evenly distributed between the top-tier switches. If one of the top tier switches were to fail, it only slightly degrades performance through the data center.
Reference: Clos Networks: What's Old Is New Again, What goes around, comes around – Clos Networks are back
http://www.networkworld.com/article/2226122/cisco-subnet/clos-networks--what-s-old-is-new-again.html
Question 10
A company needs a simple guest access solution. On each HP Provision access layer switch, the network administrator (Web-Auth) to an external Web server.
Which guidelines must the administrator follow while setting up the Web server?
- The Web server must be able to ping IP addresses in the Web-Auth subnet on each switch.
- The server must have a certificate that is signed by a CA certificate loaded on the access layer switches.
- The login pages must exactly match template pages provided by HP. with the exception of the logo image.
- The login pages must use specific names, which are documented in switch manuals.
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
Incorrect Not B: No certificate is required.Not C, D: . Specifying the URL for Web-Auth Pages That Are Stored on an External Web Server Under External Web Pages, specify the correct URL for each page. a. In the Login Page URL field, specify the URL of the login page, which users see when they try to access a Web site. For example, you might enter a URL such as http://192.168.1.1/login.html or http:// www.yourcompany.com/login.html. b. In the Welcome Page URL field, specify the URL of the welcome page that users see if they log in successfully. c. In the Failed Page URL, specify the URL of the page that users see if they do not enter a valid username and password or if a RADIUS server is unavailable. Reference: Web Authentication for Mobile Usersftp://ftp.hp.com/pub/networking/software/08-C05-WebAuth.pdf Incorrect
Not B: No certificate is required.
Not C, D: . Specifying the URL for Web-Auth Pages That Are Stored on an External Web Server
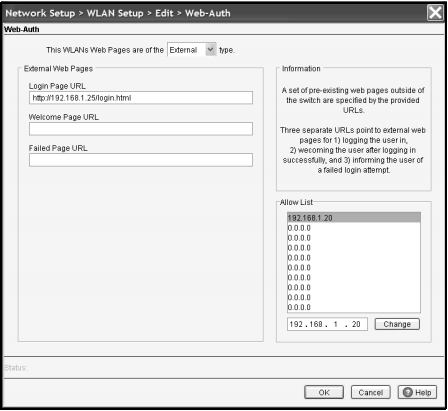
Under External Web Pages, specify the correct URL for each page.
a. In the Login Page URL field, specify the URL of the login page, which users see when they try to access a Web site. For example, you might enter a URL such as http://192.168.1.1/login.html or http:// www.yourcompany.com/login.html.
b. In the Welcome Page URL field, specify the URL of the welcome page that users see if they log in successfully.
c. In the Failed Page URL, specify the URL of the page that users see if they do not enter a valid username and password or if a RADIUS server is unavailable.
Reference: Web Authentication for Mobile Users
ftp://ftp.hp.com/pub/networking/software/08-C05-WebAuth.pdf
HOW TO OPEN VCE FILES
Use VCE Exam Simulator to open VCE files

HOW TO OPEN VCEX AND EXAM FILES
Use ProfExam Simulator to open VCEX and EXAM files


ProfExam at a 20% markdown
You have the opportunity to purchase ProfExam at a 20% reduced price
Get Now!




