Download CompTIA Linux+ Certification Exam.XK0-005.VCEplus.2024-08-03.94q.vcex
| Vendor: | CompTIA |
| Exam Code: | XK0-005 |
| Exam Name: | CompTIA Linux+ Certification Exam |
| Date: | Aug 03, 2024 |
| File Size: | 2 MB |
| Downloads: | 6 |
How to open VCEX files?
Files with VCEX extension can be opened by ProfExam Simulator.
Discount: 20%
Demo Questions
Question 1
A Linux system fails to start and delivers the following error message:

Which of the following commands can be used to address this issue?
- fsck.ext4 /dev/sda1
- partprobe /dev/sda1
- fdisk /dev/sda1
- mkfs.ext4 /dev/sda1
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
The command fsck.ext4 /dev/sda1 can be used to address the issue. The issue is caused by a corrupted filesystem on the /dev/sda1 partition. The error message shows that the filesystem type is ext4 and the superblock is invalid. The command fsck.ext4 is a tool for checking and repairing ext4 filesystems. The command will scan the partition for errors and attempt to fix them. This command can resolve the issue and allow the system to start.The other options are incorrect because they either do not fix the filesystem (partprobe or fdisk) or destroy the data on the partition (mkfs.ext4). Reference: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 10: Managing Storage, page 325. The command fsck.ext4 /dev/sda1 can be used to address the issue. The issue is caused by a corrupted filesystem on the /dev/sda1 partition. The error message shows that the filesystem type is ext4 and the superblock is invalid. The command fsck.ext4 is a tool for checking and repairing ext4 filesystems. The command will scan the partition for errors and attempt to fix them. This command can resolve the issue and allow the system to start.
The other options are incorrect because they either do not fix the filesystem (partprobe or fdisk) or destroy the data on the partition (mkfs.ext4). Reference: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 10: Managing Storage, page 325.
Question 2
Based on an organization's new cybersecurity policies, an administrator has been instructed to ensure that, by default, all new users and groups that are created fall within the specified values below.

To which of the following configuration files will the required changes need to be made?
- /etc/login.defs
- /etc/security/limits.conf
- /etc/default/useradd
- /etc/profile
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
The required changes need to be made to the /etc/login.defs configuration file. The /etc/login.defs file defines the default values for user and group IDs, passwords, shells, and other parameters for user and group creation.The file contains the directives UID_MIN, UID_MAX, GID_MIN, and GID_MAX, which set the minimum and maximum values for automatic user and group ID selection. The administrator can edit this file and change the values to match the organization's new cybersecurity policies. This is the correct file to modify to accomplish the task. The other options are incorrect because they either do not affect the user and group IDs (/etc/security/limits.conf or /etc/profile) or do not set the default values (/etc/default/useradd). Reference: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 15: Managing Users and Groups, page 463. The required changes need to be made to the /etc/login.defs configuration file. The /etc/login.defs file defines the default values for user and group IDs, passwords, shells, and other parameters for user and group creation.
The file contains the directives UID_MIN, UID_MAX, GID_MIN, and GID_MAX, which set the minimum and maximum values for automatic user and group ID selection. The administrator can edit this file and change the values to match the organization's new cybersecurity policies. This is the correct file to modify to accomplish the task. The other options are incorrect because they either do not affect the user and group IDs (/etc/security/limits.conf or /etc/profile) or do not set the default values (/etc/default/useradd). Reference: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 15: Managing Users and Groups, page 463.
Question 3
A Linux administrator is trying to remove the ACL from the file /home/user/dat a. txt but receives the following error message:
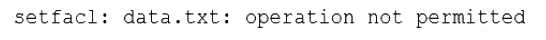
Given the following analysis:

Which of the following is causing the error message?
- The administrator is not using a highly privileged account.
- The filesystem is mounted with the wrong options.
- SELinux file context is denying the ACL changes.
- File attributes are preventing file modification.
Correct answer: D
Explanation:
File attributes are preventing file modification, which is causing the error message. The output of lsattr /home/user/data.txt shows that the file has the immutable attribute (i) set, which means that the file cannot be changed, deleted, or renamed. The command setfacl -b /home/user/data.txt tries to remove the ACL from the file, but fails because of the immutable attribute. The administrator needs to remove the immutable attribute first by using the command chattr -i /home/user/data.txt and then try to remove the ACL again. The other options are incorrect because they are not supported by the outputs. The administrator is using a highly privileged account, as shown by the # prompt. The filesystem is mounted with the correct options, as shown by the output of mount | grep /home. SELinux file context is not denying the ACL changes, as shown by the output of ls -Z /home/user/data.txt. Reference: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 11: Managing Files and Directories, pages 357-358. File attributes are preventing file modification, which is causing the error message. The output of lsattr /home/user/data.txt shows that the file has the immutable attribute (i) set, which means that the file cannot be changed, deleted, or renamed. The command setfacl -b /home/user/data.txt tries to remove the ACL from the file, but fails because of the immutable attribute. The administrator needs to remove the immutable attribute first by using the command chattr -i /home/user/data.txt and then try to remove the ACL again. The other options are incorrect because they are not supported by the outputs. The administrator is using a highly privileged account, as shown by the # prompt. The filesystem is mounted with the correct options, as shown by the output of mount | grep /home. SELinux file context is not denying the ACL changes, as shown by the output of ls -Z /home/user/data.txt. Reference: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 11: Managing Files and Directories, pages 357-358.
Question 4
A Linux administrator needs to create a new cloud.cpio archive containing all the files from the current directory. Which of the following commands can help to accomplish this task?
- ls | cpio -iv > cloud.epio
- ls | cpio -iv < cloud.epio
- ls | cpio -ov > cloud.cpio
- ls cpio -ov < cloud.cpio
Correct answer: C
Explanation:
The command ls | cpio -ov > cloud.cpio can help to create a new cloud.cpio archive containing all the files from the current directory. The ls command lists the files in the current directory and outputs them to the standard output. The | operator pipes the output to the next command.The cpio command is a tool for creating and extracting compressed archives. The -o option creates a new archive and the -v option shows the verbose output. The > operator redirects the output to the cloud.cpio file. This command will create a new cloud.cpio archive with all the files from the current directory. The other options are incorrect because they either use the wrong options (-i instead of -o), the wrong arguments (cloud.epio instead of cloud.cpio), or the wrong syntax (< instead of > or missing |). Reference: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 11: Managing Files and Directories, page 351. The command ls | cpio -ov > cloud.cpio can help to create a new cloud.cpio archive containing all the files from the current directory. The ls command lists the files in the current directory and outputs them to the standard output. The | operator pipes the output to the next command.
The cpio command is a tool for creating and extracting compressed archives. The -o option creates a new archive and the -v option shows the verbose output. The > operator redirects the output to the cloud.cpio file. This command will create a new cloud.cpio archive with all the files from the current directory. The other options are incorrect because they either use the wrong options (-i instead of -o), the wrong arguments (cloud.epio instead of cloud.cpio), or the wrong syntax (< instead of > or missing |). Reference: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 11: Managing Files and Directories, page 351.
Question 5
A systems administrator made some changes in the ~/.bashrc file and added an alias command.
When the administrator tried to use the alias command, it did not work. Which of the following should be executed FIRST?
- source ~/.bashrc
- read ~/.bashrc
- touch ~/.bashrc
- echo ~/.bashrc
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
The command source ~/.bashrc should be executed first to use the alias command.The source command reads and executes commands from a file in the current shell environment.The ~/.bashrc file is a configuration file that contains commands and aliases that are executed when a new bash shell is started. The administrator made some changes in the ~/.bashrc file and added an alias command, but the changes are not effective until the file is sourced or a new shell is started.The command source ~/.bashrc will reload the file and make the alias command available. The other options are incorrect because they either do not execute the commands in the file (read, touch, or echo) or do not affect the current shell environment (read or echo). Reference: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 9: Working with the Linux Shell, page 295. The command source ~/.bashrc should be executed first to use the alias command.
The source command reads and executes commands from a file in the current shell environment.
The ~/.bashrc file is a configuration file that contains commands and aliases that are executed when a new bash shell is started. The administrator made some changes in the ~/.bashrc file and added an alias command, but the changes are not effective until the file is sourced or a new shell is started.
The command source ~/.bashrc will reload the file and make the alias command available. The other options are incorrect because they either do not execute the commands in the file (read, touch, or echo) or do not affect the current shell environment (read or echo). Reference: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 9: Working with the Linux Shell, page 295.
Question 6
A junior systems administrator has just generated public and private authentication keys for passwordless login. Which of the following files will be moved to the remote servers?
- id_dsa.pem
- id_rsa
- id_ecdsa
- id_rsa.pub
Correct answer: D
Explanation:
The file id_rsa.pub will be moved to the remote servers for passwordless login. The id_rsa.pub file is the public authentication key that is generated by the ssh-keygen command. The public key can be copied to the remote servers by using the ssh-copy-id command or manually. The remote servers will use the public key to authenticate the user who has the corresponding private key (id_rsa). This will allow the user to log in without entering a password. The other options are incorrect because they are either private keys (id_rsa, id_dsa.pem, or id_ecdsa) or non-existent files (id_dsa.pem or id_ecdsa). Reference: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide,Chapter 13: Managing Network Services, page 410. The file id_rsa.pub will be moved to the remote servers for passwordless login. The id_rsa.pub file is the public authentication key that is generated by the ssh-keygen command. The public key can be copied to the remote servers by using the ssh-copy-id command or manually. The remote servers will use the public key to authenticate the user who has the corresponding private key (id_rsa). This will allow the user to log in without entering a password. The other options are incorrect because they are either private keys (id_rsa, id_dsa.pem, or id_ecdsa) or non-existent files (id_dsa.pem or id_ecdsa). Reference: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide,
Chapter 13: Managing Network Services, page 410.
Question 7
An administrator accidentally deleted the /boot/vmlinuz file and must resolve the issue before the server is rebooted. Which of the following commands should the administrator use to identify the correct version of this file?
- rpm -qa | grep kernel; uname -a
- yum -y update; shutdown -r now
- cat /etc/centos-release; rpm -Uvh --nodeps
- telinit 1; restorecon -Rv /boot
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
The command rpm -qa | grep kernel lists all the installed kernel packages, and the command uname -a displays the current kernel version. These commands can help the administrator identify the correct version of the /boot/vmlinuz file, which is the kernel image file. The other options are not relevant or helpful for this task. Reference: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 8: Managing the Linux Boot Process, page 267. The command rpm -qa | grep kernel lists all the installed kernel packages, and the command uname -a displays the current kernel version. These commands can help the administrator identify the correct version of the /boot/vmlinuz file, which is the kernel image file. The other options are not relevant or helpful for this task. Reference: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 8: Managing the Linux Boot Process, page 267.
Question 8
A cloud engineer needs to change the secure remote login port from 22 to 49000. Which of the following files should the engineer modify to change the port number to the desired value?
- /etc/host.conf
- /etc/hostname
- /etc/services
- /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Correct answer: D
Explanation:
The file /etc/ssh/sshd_config contains the configuration settings for the SSH daemon, which handles the secure remote login. To change the port number, the engineer should edit this file and modify the line that says Port 22 to Port 49000. The other files are not related to the SSH service. Reference: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 13: Managing Network Services, page 411. The file /etc/ssh/sshd_config contains the configuration settings for the SSH daemon, which handles the secure remote login. To change the port number, the engineer should edit this file and modify the line that says Port 22 to Port 49000. The other files are not related to the SSH service. Reference: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 13: Managing Network Services, page 411.
Question 9
A new file was added to a main Git repository. An administrator wants to synchronize a local copy with the contents of the main repository. Which of the following commands should the administrator use for this task?
- git reflog
- git pull
- git status
- git push
Correct answer: B
Explanation:
The command iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 80 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.0.2.25:3128 adds a rule to the nat table that redirects all incoming TCP packets with destination port 80 (HTTP) to the proxy server 192.0.2.25 on port 3128. This is the correct way to achieve the task. The other options are incorrect because they either delete a rule (-D), use the wrong protocol (top instead of tcp), or use the wrong port (81 instead of 80).Reference: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 12: Managing Network Connections, page 381. The command iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 80 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.0.2.25:3128 adds a rule to the nat table that redirects all incoming TCP packets with destination port 80 (HTTP) to the proxy server 192.0.2.25 on port 3128. This is the correct way to achieve the task. The other options are incorrect because they either delete a rule (-D), use the wrong protocol (top instead of tcp), or use the wrong port (81 instead of 80).
Reference: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 12: Managing Network Connections, page 381.
Question 10
A Linux administrator needs to redirect all HTTP traffic temporarily to the new proxy server 192.0.2.25 on port 3128. Which of the following commands will accomplish this task?
- iptables -t nat -D PREROUTING -p tcp --sport 80 -j DNAT - -to-destination 192.0.2.25:3128
- iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p top --dport 81 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.0.2.25:3129
- iptables -t nat -I PREROUTING -p top --sport 80 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.0.2.25:3129
- iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 80 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.0.2.25:3128
Correct answer: D
Explanation:
The command iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 80 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.0.2.25:3128 adds a rule to the nat table that redirects all incoming TCP packets with destination port 80 (HTTP) to the proxy server 192.0.2.25 on port 3128. This is the correct way to achieve the task. The other options are incorrect because they either delete a rule (-D), use the wrong protocol (top instead of tcp), or use the wrong port (81 instead of 80).Reference: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 12: Managing Network Connections, page 381. The command iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 80 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.0.2.25:3128 adds a rule to the nat table that redirects all incoming TCP packets with destination port 80 (HTTP) to the proxy server 192.0.2.25 on port 3128. This is the correct way to achieve the task. The other options are incorrect because they either delete a rule (-D), use the wrong protocol (top instead of tcp), or use the wrong port (81 instead of 80).
Reference: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 12: Managing Network Connections, page 381.
HOW TO OPEN VCE FILES
Use VCE Exam Simulator to open VCE files

HOW TO OPEN VCEX AND EXAM FILES
Use ProfExam Simulator to open VCEX and EXAM files


ProfExam at a 20% markdown
You have the opportunity to purchase ProfExam at a 20% reduced price
Get Now!



