Download Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies (SPCOR).350-501.NewDumps.2021-02-14.31q.vcex
| Vendor: | Cisco |
| Exam Code: | 350-501 |
| Exam Name: | Implementing and Operating Cisco Service Provider Network Core Technologies (SPCOR) |
| Date: | Feb 14, 2021 |
| File Size: | 2 MB |
| Downloads: | 2 |
How to open VCEX files?
Files with VCEX extension can be opened by ProfExam Simulator.
Discount: 20%
Demo Questions
Question 1
Which control plane protocol is used between Cisco SD-WAN routers and vSmart controllers?
- BGP
- OMP
- TCP
- UDP
Correct answer: B
Explanation:
Cisco SD-WAN uses Overlay Management Protocol (OMP) which manages the overlay network. OMP runs between the vSmart controllers and WAN Edge routers (and among vSmarts themselves) where control plane information, such as the routing, policy, and management information, is exchanged over a secure connection. Cisco SD-WAN uses Overlay Management Protocol (OMP) which manages the overlay network. OMP runs between the vSmart controllers and WAN Edge routers (and among vSmarts themselves) where control plane information, such as the routing, policy, and management information, is exchanged over a secure connection.

Question 2
In a Cisco Catalyst switch equipped with two supervisor modules an administrator must temporally remove the active supervisor from the chassis to perform hardware maintenance on it.
Which mechanism ensure that the active supervisor removal is not disruptive to the network operation?
- NSF/NSR
- SSO
- HSRP
- VRRP
Correct answer: B
Explanation:
Stateful Switchover (SSO) provides protection for network edge devices with dual Route Processors (RPs) that represent a single point of failure in the network design, and where an outage might result in loss of service for customers. Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/lan/catalyst6500/ios/12-2SY/configuration/guide/sy_swcg/stateful_switchover.html Stateful Switchover (SSO) provides protection for network edge devices with dual Route Processors (RPs) that represent a single point of failure in the network design, and where an outage might result in loss of service for customers.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/lan/catalyst6500/ios/12-2SY/configuration/guide/sy_swcg/stateful_switchover.html
Question 3
Which router is elected the IGMP Querier when more than one router is in the same LAN segment?
- The router with the shortest uptime
- The router with the lowest IP address
- The router with the highest IP address
- The router with the longest uptime
Correct answer: B
Explanation:
Query messages are used to elect the IGMP querier as follows: When IGMPv2 devices start, they each multicast a general query message to the all-systems group address of 224.0.0.1 with their interface address in the source IP address field of the message. When an IGMPv2 device receives a general query message, the device compares the source IP address in the message with its own interface address. The device with the lowest IP address on the subnet is elected the IGMP querier. All devices (excluding the querier) start the query timer, which is reset whenever a general query message is received from the IGMP querier. If the query timer expires, it is assumed that the IGMP querier has gone down, and the election process is performed again to elect a new IGMP querier. Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/lan/catalyst3750x_3560x/software/release/15-2_2_e/multicast/configuration_guide/b_mc_1522e_3750x_3560x_cg/b_ipmc_3750x_3560x_chapter_01000.html Query messages are used to elect the IGMP querier as follows:
- When IGMPv2 devices start, they each multicast a general query message to the all-systems group address of 224.0.0.1 with their interface address in the source IP address field of the message.
- When an IGMPv2 device receives a general query message, the device compares the source IP address in the message with its own interface address. The device with the lowest IP address on the subnet is elected the IGMP querier.
- All devices (excluding the querier) start the query timer, which is reset whenever a general query message is received from the IGMP querier. If the query timer expires, it is assumed that the IGMP querier has gone down, and the election process is performed again to elect a new IGMP querier.
Reference:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/lan/catalyst3750x_3560x/software/release/15-2_2_e/multicast/configuration_guide/b_mc_1522e_3750x_3560x_cg/b_ipmc_3750x_3560x_chapter_01000.html
Question 4
Refer to the exhibit.
ip sla 10
icmp-echo 192.168.10.20
timeout 500
frequency 3
ip sla schedule 10 life forever start-time now
track 10 ip sla 10 reachability
The IP SLA is configured in a router. An engineer must configure an EEM applet to shut down the interface and bring it back up when there is a problem with the IP SLA. Which configuration should the engineer use?
- event manager applet EEM_IP_SLAevent track 10 state down
- event manager applet EEM_IP_SLAevent track 10 state unreachable
- event manager applet EEM_IP_SLAevent sla 10 state unreachable
- event manager applet EEM_IP_SLAevent sla 10 state down
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
The “ip sla 10” will ping the IP 192.168.10.20 every 3 seconds to make sure the connection is still up. We can configure an EEM applet if there is any problem with this IP SLA via the command “event track 10 state down”. Reference: https://www.theroutingtable.com/ip-sla-and-cisco-eem/ The “ip sla 10” will ping the IP 192.168.10.20 every 3 seconds to make sure the connection is still up. We can configure an EEM applet if there is any problem with this IP SLA via the command “event track 10 state down”.
Reference: https://www.theroutingtable.com/ip-sla-and-cisco-eem/
Question 5
A network engineer is configuring Flexible NetFlow and enters these commands:
Sampler Netflow1
mode random one-out-of 100
interface fastethernet 1/0
flow-sampler netflow1
Which are two results of implementing this feature instead of traditional NetFlow? (Choose two)
- Only the flows of top 100 talkers are exported
- CPU and memory utilization are reduced
- The data export flow is more secure
- The accuracy of the data to be analyzed is improved
- The number of packets to be analyzed are reduced
Correct answer: BE
Explanation:
The “mode random one-out of 100” specifies that sampling uses the random mode and only take one sample out of every 100 packets. The “mode random one-out of 100” specifies that sampling uses the random mode and only take one sample out of every 100 packets.
Question 6
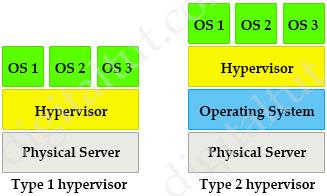
What is a benefit of using a Type 2 hypervisor instead of a Type 1 hypervisor?
- ability to operate on hardware that is running other OSs
- improved security because the underlying OS is eliminated
- improved density and scalability
- better application performance
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
There are two types of hypervisors: type 1 and type 2 hypervisor. In type 1 hypervisor (or native hypervisor), the hypervisor is installed directly on the physical server. Then instances of an operating system (OS) are installed on the hypervisor. Type 1 hypervisor has direct access to the hardware resources. Therefore they are more efficient than hosted architectures. Some examples of type 1 hypervisor are VMware vSphere/ESXi, Oracle VM Server, KVM and Microsoft Hyper-V. In contrast to type 1 hypervisor, a type 2 hypervisor (or hosted hypervisor) runs on top of an operating system and not the physical hardware directly. A big advantage of Type 2 hypervisors is that management console software is not required. Examples of type 2 hypervisor are VMware Workstation (which can run on Windows, Mac and Linux) or Microsoft Virtual PC (only runs on Windows). Type 1 is more efficient and well performing, it is also more secure than type 2 because the flaws and vulnerabilities that are endemic to Operating Systems are often absent from Type 1, bare metal hypervisors. Type 1 has better performance, scalability and stability but supported by limited hardware. There are two types of hypervisors: type 1 and type 2 hypervisor.
In type 1 hypervisor (or native hypervisor), the hypervisor is installed directly on the physical server. Then instances of an operating system (OS) are installed on the hypervisor. Type 1 hypervisor has direct access to the hardware resources. Therefore they are more efficient than hosted architectures. Some examples of type 1 hypervisor are VMware vSphere/ESXi, Oracle VM Server, KVM and Microsoft Hyper-V.
In contrast to type 1 hypervisor, a type 2 hypervisor (or hosted hypervisor) runs on top of an operating system and not the physical hardware directly. A big advantage of Type 2 hypervisors is that management console software is not required. Examples of type 2 hypervisor are VMware Workstation (which can run on Windows, Mac and Linux) or Microsoft Virtual PC (only runs on Windows).
Type 1 is more efficient and well performing, it is also more secure than type 2 because the flaws and vulnerabilities that are endemic to Operating Systems are often absent from Type 1, bare metal hypervisors. Type 1 has better performance, scalability and stability but supported by limited hardware.
Question 7
In a wireless Cisco SD-Access deployment, which roaming method is used when a user moves from one access point to another on a different access switch using a single WLC?
- Layer 3
- inter-xTR
- auto anchor
- fast roam
Correct answer: D
Question 8
Which DHCP option provides the CAPWAP APs with the address of the wireless controller(s)?
- 43
- 66
- 69
- 150
Correct answer: A
Question 9
An engineer must configure HSRP group 300 on a Cisco IOS router. When the router is functional, it must be the active HSRP router. The peer router has been configured using the default priority value. Which three commands are required? (Choose three)
- standby 300 timers 1 110
- standby 300 priority 90
- standby 300 priority 110
- standby version 2
- standby version 1
- standby 300 preempt
Correct answer: CDF
Question 10
In a traditional 3 tier topology, an engineer must explicitly configure a switch as the root bridge and exclude it from any further election process for the spanning-tree domain. Which action accomplishes this task?
- Configure the spanning-tree priority to 32768
- Configure root guard and portfast on all access switch ports
- Configure BPDU guard in all switch-to-switch connections
- Configure the spanning-tree priority equal to 0
Correct answer: B
Explanation:
Root guard does not allow the port to become a STP root port, so the port is always STP-designated. If a better BPDU arrives on this port, root guard does not take the BPDU into account and elect a new STP root. Instead, root guard puts the port into the root-inconsistent STP state which is equal to a listening state. No traffic is forwarded across this port. Below is an example of where to configure Root Guard on the ports. Notice that Root Guard is always configure on designated ports. To configure Root Guard use this command: Switch(config-if)# spanning-tree guard root Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/lan-switching/spanning-tree-protocol/10588-74.html Root guard does not allow the port to become a STP root port, so the port is always STP-designated. If a better BPDU arrives on this port, root guard does not take the BPDU into account and elect a new STP root. Instead, root guard puts the port into the root-inconsistent STP state which is equal to a listening state. No traffic is forwarded across this port.
Below is an example of where to configure Root Guard on the ports. Notice that Root Guard is always configure on designated ports.

To configure Root Guard use this command:
Switch(config-if)# spanning-tree guard root
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/lan-switching/spanning-tree-protocol/10588-74.html
HOW TO OPEN VCE FILES
Use VCE Exam Simulator to open VCE files

HOW TO OPEN VCEX AND EXAM FILES
Use ProfExam Simulator to open VCEX and EXAM files


ProfExam at a 20% markdown
You have the opportunity to purchase ProfExam at a 20% reduced price
Get Now!



