Download Implementing Cisco Enterprise Network Core Technologies (350-401 ENCOR).350-401.CertDumps.2021-09-24.168q.vcex
| Vendor: | Cisco |
| Exam Code: | 350-401 |
| Exam Name: | Implementing Cisco Enterprise Network Core Technologies (350-401 ENCOR) |
| Date: | Sep 24, 2021 |
| File Size: | 6 MB |
How to open VCEX files?
Files with VCEX extension can be opened by ProfExam Simulator.
Discount: 20%
Demo Questions
Question 1
Which PAgP mode combination prevents an Etherchannel from forming?
- auto/auto
- desirable/desirable
- auto/desirable
- desirable
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
There are two PAgP modes:Auto Responds to PAgP messages but does not aggressively negotiate a PAgP EtherChannel. A channel is formed only if the port on the other end is set to Desirable. This is the default mode. Desirable Port actively negotiates channeling status with the interface on the other end of the link. A channel is formed if the other side is Auto or Desirable. The table below lists if an EtherChannel will be formed or not for PAgP:PAgP Desirable Auto Desirable Yes Yes Auto Yes No There are two PAgP modes:
Auto Responds to PAgP messages but does not aggressively negotiate a PAgP EtherChannel. A channel is formed only if the port on the other end is set to Desirable. This is the default mode.
Desirable Port actively negotiates channeling status with the interface on the other end of the link. A channel is formed if the other side is Auto or Desirable.
The table below lists if an EtherChannel will be formed or not for PAgP:
PAgP Desirable Auto
Desirable Yes Yes
Auto Yes No
Question 2
Refer to the exhibit. A port channel is configured between SW2 and SW3. SW2 is not running Cisco operating system. When all physical connections are mode, the port channel does not establish. Based on the configuration excerpt of SW3, what is the cause of the problem?
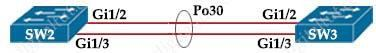
interface gi1/2
channel-group 30 mode desirable
port-channel load-balance src-ip
interface gi1/3
channel-group 30 mode desirable
port-channel load-balance src-ip
interface PortChannel 30
switchport mode trunk
switchport encapsulation dot1q
switchport trunk allowed vlan 10-100
- The port channel on SW2 is using an incompatible protocol
- The port-channel trunk is not allowing the native VLAN
- The port-channel should be set to auto
- The port-channel interface lead balance should be set to src-mac
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
The Cisco switch was configured with PAgP, which is a Cisco proprietary protocol so non-Cisco switch could not communicate. The Cisco switch was configured with PAgP, which is a Cisco proprietary protocol so non-Cisco switch could not communicate.
Question 3
Refer to exhibit. VLANs 50 and 60 exist on the trunk links between all switches. All access ports on SW3 are configured for VLAN 50 and SW1 is the VTP server. Which command ensures that SW3 receives frames only from VLAN 50?

- SW1 (config)#vtp pruning
- SW3(config)#vtp mode transparent
- SW2(config)=vtp pruning
- SW1(config)>vtp mode transparent
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
SW3 does not have VLAN 60 so it should not receive traffic for this VLAN (sent from SW2). Therefore we should configure VTP Pruning on SW3 so that SW2 does not forward VLAN 60 traffic to SW3. SW3 does not have VLAN 60 so it should not receive traffic for this VLAN (sent from SW2). Therefore we should configure VTP Pruning on SW3 so that SW2 does not forward VLAN 60 traffic to SW3.
Question 4
Refer to the exhibit. SwitchC connects HR and Sales to the Core switch. However, business needs require that no traffic from the Finance VLAN traverse this switch. Which command meets this requirement?
SwitchC#show vtp status
VTP Version : 2
Configuration Revision : 0
Maximum VLANs supported locally : 255
Number of existing VLANs : 8
VTP Operating Mode : Transparent
VTP Domain Name : MyDomain.com
VTP Pruning Mode : Disabled
VTP V2 Mode : Disabled
VTP Traps Generation : Disabled
MD5 digest : 0xCC 0x77 0x02 0x40 0x93 0xB5 0xC1 0xA2
Configuration last modified by 0.0.0.0 at 3-1-93 00:00:00
SwitchC#show vlan brief
VLAN Name Status Ports
---- -------------------------------- --------- ------------------------------- 1 default active Fa0/3, Fa0/4, Fa0/5, Fa0/6
Fa0/7, Fa0/8, Fa0/9, Fa0/10
Fa0/11, Fa0/12, Fa0/13, Fa0/14
Fa0/15, Fa0/16, Fa0/17, Fa0/18
Fa0/19, Fa0/20, Fa0/21, Fa0/22
Fa0/23, Fa0/24, Po1
110 Finance active
210 HR active Fa0/1
310 Sales active Fa0/2
SwitchC#show int trunk
Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan
Gig1/1 on 802.1q trunking 1
Gig1/2 on 802.1q trunking 1
Port Vlans allowed on trunk
Gig1/1 1-1005
Gig1/2 1-1005
Port Vlans allowed and active in m anagement domain
Gig1/1 1,110,210,310
Gig1/2 1,110,210,310
SwitchC#show run interface port-channel 1
interface Port-channel 1
description Uplink_to_Core
switchport mode trunk
- SwitchC(config)#vtp pruning
- SwitchC(config)#vtp pruning vlan 110
- SwitchC(config)#interface port-channel 1SwitchC(config-if)#switchport trunk allowed vlan add 210,310
- SwitchC(config)#interface port-channel 1SwitchC(config-if)#switchport trunk allowed vlan remove 110
Correct answer: D
Explanation:
From the "show vlan brief" we learn that Finance belongs to VLAN 110 and all VLANs (from 1 to 1005) are allowed to traverse the trunk (port-channel 1). Therefore we have to remove VLAN 110 from the allowed VLAN list with the "switchport trunk allowed vlan remove " command. The pruning feature cannot do this job as Finance VLAN is active. Three major building blocks that make up SDA: the control plane, the data plane and the policy plane.SD-Access + Control-Plane based on LISP + Data-Plane based on VXLAN + Policy-Plane based on TrustSec From the "show vlan brief" we learn that Finance belongs to VLAN 110 and all VLANs (from 1 to 1005) are allowed to traverse the trunk (port-channel 1). Therefore we have to remove VLAN 110 from the allowed VLAN list with the "switchport trunk allowed vlan remove " command. The pruning feature cannot do this job as Finance VLAN is active.
Three major building blocks that make up SDA: the control plane, the data plane and the policy plane.
SD-Access
+ Control-Plane based on LISP
+ Data-Plane based on VXLAN
+ Policy-Plane based on TrustSec
Question 5
Which function does a fabric edge node perform in an SD-Access deployment?
- Connects the SD-Access fabric to another fabric or external Layer 3 networks
- Connects endpoints to the fabric and forwards their traffic
- Provides reachability border nodes in the fabric underlay
- Encapsulates end-user data traffic into LISP.
Correct answer: B
Explanation:
There are five basic device roles in the fabric overlay:+ Control plane node: This node contains the settings, protocols, and mapping tables to provide the endpoint-to-location (EID-to-RLOC) mapping system for the fabric overlay. + Fabric border node: This fabric device (for example, core layer device) connects external Layer 3 networks to the SDA fabric.+ Fabric edge node: This fabric device (for example, access or distribution layer device) connects wired endpoints to the SDA fabric.+ Fabric WLAN controller (WLC): This fabric device connects APs and wireless endpoints to the SDA fabric.+ Intermediate nodes: These are intermediate routers or extended switches that do not provide any sort of SD-Access fabric role other than underlay services. Reference: CCNP and CCIE Enterprise Core ENCOR 350-401 Official Cert Guide There are five basic device roles in the fabric overlay:
+ Control plane node: This node contains the settings, protocols, and mapping tables to provide the endpoint-to-location (EID-to-RLOC) mapping system for the fabric overlay.
+ Fabric border node: This fabric device (for example, core layer device) connects external Layer 3 networks to the SDA fabric.
+ Fabric edge node: This fabric device (for example, access or distribution layer device) connects wired endpoints to the SDA fabric.
+ Fabric WLAN controller (WLC): This fabric device connects APs and wireless endpoints to the SDA fabric.
+ Intermediate nodes: These are intermediate routers or extended switches that do not provide any sort of SD-Access fabric role other than underlay services.
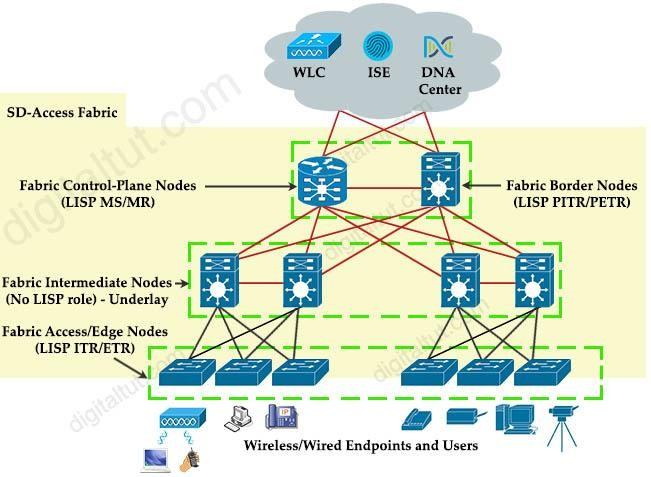
Reference: CCNP and CCIE Enterprise Core ENCOR 350-401 Official Cert Guide
Question 6
Which action is the vSmart controller responsible for in an SD-WAN deployment?
- onboard vEdge nodes into the SD-WAN fabric
- distribute security information for tunnel establishment between vEdge routers
- manage, maintain, and gather configuration and status for nodes within the SD-WAN fabric
- gather telemetry data from vEdge routers
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
The major components of the vSmart controller are:+ Control plane connections Each vSmart controller establishes and maintains a control plane connection with each vEdge router in the overlay network. (In a network with multiple vSmart controllers, a single vSmart controller may have connections only to a subset of the vEdge routers, for load-balancing purposes.) Each connection, which runs as a DTLS tunnel, is established after device authentication succeeds, and it carries the encrypted payload between the vSmart controller and the vEdge router. This payload consists of route information necessary for the vSmart controller to determine the network topology, and then to calculate the best routes to network destinations and distribute this route information to the vEdge routers. The DTLS connection between a vSmart controller and a vEdge router is a permanent connection. The vSmart controller has no direct peering relationships with any devices that a vEdge router is connected to on the service side (so answer C is not correct as vSmart only manages vEdge routers only, not the whole nodes within SD-WAN fabric). + OMP (Overlay Management Protocol) The OMP protocol is a routing protocol similar to BGP that manages the Cisco SD-WAN overlay network. OMP runs inside DTLS control plane connections and carries the routes, next hops, keys, and policy information needed to establish and maintain the overlay network. OMP runs between the vSmart controller and the vEdge routers and carries only control plane information. The vSmart controller processes the routes and advertises reachability information learned from these routes to other vEdge routers in the overlay network. + Authentication The vSmart controller has pre-installed credentials that allow it to authenticate every new vEdge router that comes online (-> Answer A is correct). These credentials ensure that only authenticated devices are allowed access to the network. + Key reflection and rekeying The vSmart controller receives data plane keys from a vEdge router and reflects them to other relevant vEdge routers that need to send data plane traffic. + Policy engine The vSmart controller provides rich inbound and outbound policy constructs to manipulate routing information, access control, segmentation, extranets, and other network needs. + Netconf and CLI Netconf is a standards-based protocol used by the vManage NMS to provision a vSmart controller. In addition, each vSmart controller provides local CLI access and AAA. Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/sdwan/configuration/sdwan-xe-gs- book/system-overview.html The major components of the vSmart controller are:
+ Control plane connections Each vSmart controller establishes and maintains a control plane connection with each vEdge router in the overlay network. (In a network with multiple vSmart controllers, a single vSmart controller may have connections only to a subset of the vEdge routers, for load-balancing purposes.) Each connection, which runs as a DTLS tunnel, is established after device authentication succeeds, and it carries the encrypted payload between the vSmart controller and the vEdge router. This payload consists of route information necessary for the vSmart controller to determine the network topology, and then to calculate the best routes to network destinations and distribute this route information to the vEdge routers. The DTLS connection between a vSmart controller and a vEdge router is a permanent connection. The vSmart controller has no direct peering relationships with any devices that a vEdge router is connected to on the service side (so answer C is not correct as vSmart only manages vEdge routers only, not the whole nodes within SD-WAN fabric).
+ OMP (Overlay Management Protocol) The OMP protocol is a routing protocol similar to BGP that manages the Cisco SD-WAN overlay network. OMP runs inside DTLS control plane connections and carries the routes, next hops, keys, and policy information needed to establish and maintain the overlay network. OMP runs between the vSmart controller and the vEdge routers and carries only control plane information. The vSmart controller processes the routes and advertises reachability information learned from these routes to other vEdge routers in the overlay network.
+ Authentication The vSmart controller has pre-installed credentials that allow it to authenticate every new vEdge router that comes online (-> Answer A is correct). These credentials ensure that only authenticated devices are allowed access to the network.
+ Key reflection and rekeying The vSmart controller receives data plane keys from a vEdge router and reflects them to other relevant vEdge routers that need to send data plane traffic.
+ Policy engine The vSmart controller provides rich inbound and outbound policy constructs to manipulate routing information, access control, segmentation, extranets, and other network needs. + Netconf and CLI Netconf is a standards-based protocol used by the vManage NMS to provision a vSmart controller. In addition, each vSmart controller provides local CLI access and AAA.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/sdwan/configuration/sdwan-xe-gs- book/system-overview.html
Question 7
Which statement about a Cisco APIC controller versus a more traditional SDN controller is true?
- APIC uses a policy agent to translate policies into instructions
- APIC supports OpFlex as a Northbound protocol
- APIC does support a Southbound REST API
- APIC uses an imperative model
Correct answer: A
Explanation:
The southbound protocol used by APIC is OpFlex that is pushed by Cisco as the protocol for policy enablement across physical and virtual switches. Southbound interfaces are implemented with some called Service Abstraction Layer (SAL), which talks to the network elements via SNMP and CLI. Note: Cisco OpFlex is a southbound protocol in a software -defined network (SDN). The southbound protocol used by APIC is OpFlex that is pushed by Cisco as the protocol for policy enablement across physical and virtual switches.
Southbound interfaces are implemented with some called Service Abstraction Layer (SAL), which talks to the network elements via SNMP and CLI.
Note: Cisco OpFlex is a southbound protocol in a software -defined network (SDN).
Question 8
What the role of a fusion in an SD-Access solution?
- provides connectivity to external networks
- acts as a DNS server
- performs route leaking between user-defined virtual networks and shared services
- provides additional forwarding capacity to the fabric
Correct answer: C
Explanation:
Today the Dynamic Network Architecture Software Defined Access (DNA-SDA) solution requires a fusion router to perform VRF route leaking between user VRFs and Shared-Services, which may be in the Global routing table (GRT) or another VRF. Shared Services may consist of DHCP, Domain Name System (DNS), Network Time Protocol (NTP), Wireless LAN Controller (WLC), Identity Services Engine (ISE), DNAC components which must be made available to other virtual networks (VN's) in the Campus. Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/cloud-systems-management/dna- center/213525-sda-steps-to-configure-fusion-router.html Today the Dynamic Network Architecture Software Defined Access (DNA-SDA) solution requires a fusion router to perform VRF route leaking between user VRFs and Shared-Services, which may be in the Global routing table (GRT) or another VRF. Shared Services may consist of DHCP, Domain Name System (DNS), Network Time Protocol (NTP), Wireless LAN Controller (WLC), Identity Services Engine (ISE), DNAC components which must be made available to other virtual networks (VN's) in the Campus.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/cloud-systems-management/dna- center/213525-sda-steps-to-configure-fusion-router.html
Question 9
Which statement about a fabric access point is true?
- It is in local mode an must be connected directly to the fabric border node
- It is in FlexConnect mode and must be connected directly to the fabric border node
- It is in local mode an must connected directly to the fabric edge switch
- It is in FlexConnect mode and must be connected directly to the fabric edge switch
Correct answer: C
Explanation:
Fabric mode APs continue to support the same wireless media services that traditional APs support; apply AVC, quality of service (QoS), and other wireless policies; and establish the CAPWAP control plane to the fabric WLC. Fabric APs join as local-mode APs and must be directly connected to the fabric edge node switch to enable fabric registration events, including RLOC assignment via the fabric WLC. The fabric edge nodes use CDP to recognize APs as special wired hosts, applying special port configurations and assigning the APs to a unique overlay network within a common EID space across a fabric. The assignment allows management simplification by using a single subnet to cover the AP infrastructure at a fabric site. Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/solutions/CVD/Campus/sda-sdg-2019oct.html Fabric mode APs continue to support the same wireless media services that traditional APs support; apply AVC, quality of service (QoS), and other wireless policies; and establish the CAPWAP control plane to the fabric WLC. Fabric APs join as local-mode APs and must be directly connected to the fabric edge node switch to enable fabric registration events, including RLOC assignment via the fabric WLC. The fabric edge nodes use CDP to recognize APs as special wired hosts, applying special port configurations and assigning the APs to a unique overlay network within a common EID space across a fabric. The assignment allows management simplification by using a single subnet to cover the AP infrastructure at a fabric site.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/solutions/CVD/Campus/sda-sdg-2019oct.html
Question 10
On which protocol or technology is the fabric data plane based in Cisco SD-Access fabric?
- LISP
- IS-IS
- Cisco TrustSec
- VXLAN
Correct answer: D
Explanation:
The tunneling technology used for the fabric data plane is based on Virtual Extensible LAN (VXLAN). VXLAN encapsulation is UDP based, meaning that it can be forwarded by any IP -based network (legacy or third party) and creates the overlay network for the SD-Access fabric. Although LISP is the control plane for the SD-Access fabric, it does not use LISP data encapsulation for the data plane; instead, it uses VXLAN encapsulation because it is capable of encapsulating the original Ethernet header to perform MAC- in-IP encapsulation, while LISP does not. Using VXLAN allows the SD-Access fabric to support Layer 2 and Layer 3 virtual topologies (overlays) and the ability to operate over any IP -based network with built-in network segmentation (VRF instance/VN) and built-in group-based policy. Reference: CCNP and CCIE Enterprise Core ENCOR 350-401 Official Cert Guide The tunneling technology used for the fabric data plane is based on Virtual Extensible LAN (VXLAN). VXLAN encapsulation is UDP based, meaning that it can be forwarded by any IP -based network (legacy or third party) and creates the overlay network for the SD-Access fabric. Although LISP is the control plane for the SD-Access fabric, it does not use LISP data encapsulation for the data plane; instead, it uses VXLAN encapsulation because it is capable of encapsulating the original Ethernet header to perform MAC- in-IP encapsulation, while LISP does not. Using VXLAN allows the SD-Access fabric to support Layer 2 and Layer 3 virtual topologies (overlays) and the ability to operate over any IP -based network with built-in network segmentation (VRF instance/VN) and built-in group-based policy.
Reference: CCNP and CCIE Enterprise Core ENCOR 350-401 Official Cert Guide
HOW TO OPEN VCE FILES
Use VCE Exam Simulator to open VCE files

HOW TO OPEN VCEX AND EXAM FILES
Use ProfExam Simulator to open VCEX and EXAM files


ProfExam at a 20% markdown
You have the opportunity to purchase ProfExam at a 20% reduced price
Get Now!



