Download Cisco Certified Network Associate (200-301 CCNA).200-301.Lead2Pass.2023-10-12.423q.vcex
| Vendor: | Cisco |
| Exam Code: | 200-301 |
| Exam Name: | Cisco Certified Network Associate (200-301 CCNA) |
| Date: | Oct 12, 2023 |
| File Size: | 24 MB |
| Downloads: | 4 |
How to open VCEX files?
Files with VCEX extension can be opened by ProfExam Simulator.
Discount: 20%
Demo Questions
Question 1
Which statement correctly compares traditional networks and controller-based networks?
- Only traditional networks offer a centralized control plane
- Only traditional networks natively support centralized management
- Traditional and controller-based networks abstract policies from device configurations
- Only controller-based networks decouple the control plane and the data plane
Correct answer: D
Explanation:
Most traditional devices use a distributed architecture, in which each control plane is resided in a networking device. Therefore they need to communicate with each other via messages to work correctly.In contrast to distributed architecture, centralized (or controller-based) architectures centralizes the control of networking devices into one device, called SDN controller -> Answer D is correct. Most traditional devices use a distributed architecture, in which each control plane is resided in a networking device. Therefore they need to communicate with each other via messages to work correctly.
In contrast to distributed architecture, centralized (or controller-based) architectures centralizes the control of networking devices into one device, called SDN controller -> Answer D is correct.
Question 2
Which two actions influence the EIGRP route selection process? (Choose two)
- The router calculates the reported distance by multiplying the delay on the exiting Interface by256.
- The router calculates the best backup path to the destination route and assigns it as the feasiblesuccessor.
- The router calculates the feasible distance of all paths to the destination route
- The advertised distance is calculated by a downstream neighbor to inform the local router of thebandwidth on the link
- The router must use the advertised distance as the metric for any given route
Correct answer: BC
Explanation:
The reported distance (or advertised distance) is the cost from the neighbor to the destination. It is calculated from the router advertising the route to the network. For example in the topology below, suppose router A & B are exchanging their routing tables for the first time. Router B says "Hey, the best metric (cost) from me to IOWA is 50 and the metric from you to IOWA is 90" and advertises it to router A.Router A considers the first metric (50) as the Advertised distance. The second metric (90), which is from NEVADA to IOWA (through IDAHO), is called the Feasible distance. The reported distance is calculated in the same way of calculating the metric. By default (K1 = 1, K2 = 0, K3 = 1, K4 = 0, K5 = 0), the metric is calculated as follows: -> Answer A is not correct.Feasible successor is the backup route. To be a feasible successor, the route must have an Advertised distance (AD) less than the Feasible distance (FD) of the current successor route -> Answer B is correct.Feasible distance (FD): The sum of the AD plus the cost between the local router and the next-hop router.The router must calculate the FD of all paths to choose the best path to put into the routing table.Note: Although the new CCNA exam does not have EIGRP topic but you should learn the basic knowledge of this routing protocol. The reported distance (or advertised distance) is the cost from the neighbor to the destination. It is calculated from the router advertising the route to the network. For example in the topology below, suppose router A & B are exchanging their routing tables for the first time. Router B says "Hey, the best metric (cost) from me to IOWA is 50 and the metric from you to IOWA is 90" and advertises it to router A.
Router A considers the first metric (50) as the Advertised distance. The second metric (90), which is from NEVADA to IOWA (through IDAHO), is called the Feasible distance.
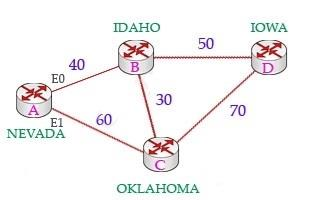
The reported distance is calculated in the same way of calculating the metric. By default (K1 = 1, K2 = 0, K3 = 1, K4 = 0, K5 = 0), the metric is calculated as follows:

-> Answer A is not correct.
Feasible successor is the backup route. To be a feasible successor, the route must have an Advertised distance (AD) less than the Feasible distance (FD) of the current successor route -> Answer B is correct.
Feasible distance (FD): The sum of the AD plus the cost between the local router and the next-hop router.
The router must calculate the FD of all paths to choose the best path to put into the routing table.
Note: Although the new CCNA exam does not have EIGRP topic but you should learn the basic knowledge of this routing protocol.
Question 3
Refer to the exhibit. What does router R1 use as its OSPF router-ID?
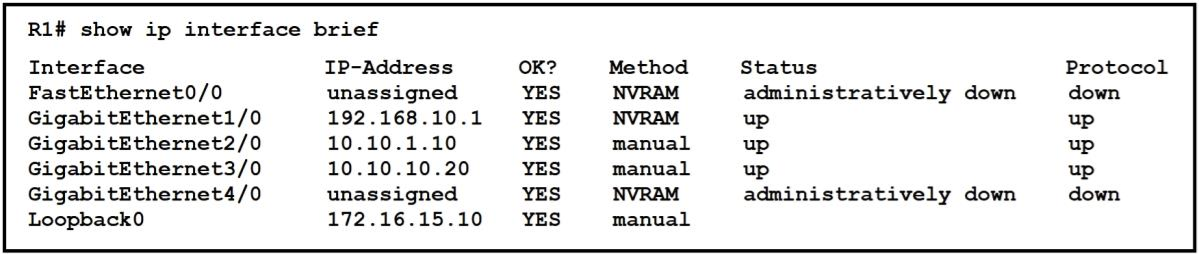
- 10.10.1.10
- 10.10.10.20
- 172.16.15.10
- 192.168.0.1
Correct answer: C
Explanation:
OSPF uses the following criteria to select the router ID:Manual configuration of the router ID (via the "router-id x.x.x.x" command under OSPF router configuration mode).Highest IP address on a loopback interface.Highest IP address on a non-loopback and active (no shutdown) interface. OSPF uses the following criteria to select the router ID:
- Manual configuration of the router ID (via the "router-id x.x.x.x" command under OSPF router configuration mode).
- Highest IP address on a loopback interface.
- Highest IP address on a non-loopback and active (no shutdown) interface.
Question 4
Which statement identifies the functionality of virtual machines?
- Virtualized servers run most efficiently when they are physically connected to a switch that isseparate from the hypervisor
- The hypervisor can virtualize physical components including CPU. memory, and storage
- Each hypervisor can support a single virtual machine and a single software switch
- The hypervisor communicates on Layer 3 without the need for additional resources
Correct answer: B
Question 5
Which option about JSON is true?
- uses predefined tags or angle brackets () to delimit markup text
- used to describe structured data that includes arrays
- used for storing information
- similar to HTML, it is more verbose than XML
Correct answer: B
Explanation:
JSON data is written as name/value pairs.A name/value pair consists of a field name (in double quotes), followed by a colon, followed by a value:"name":"Mark"JSON can use arrays. Array values must be of type string, number, object, array, boolean or null..For example:{"name":"John","age":30,"cars":[ "Ford", "BMW", "Fiat" ]} JSON data is written as name/value pairs.
A name/value pair consists of a field name (in double quotes), followed by a colon, followed by a value:
"name":"Mark"
JSON can use arrays. Array values must be of type string, number, object, array, boolean or null..
For example:
{
"name":"John",
"age":30,
"cars":[ "Ford", "BMW", "Fiat" ]
}
Question 6
Which attribute does a router use to select the best path when two or more different routes to the same destination exist from two different routing protocols?
- dual algorithm
- metric
- administrative distance
- hop count
Correct answer: C
Explanation:
Administrative distance is the feature used by routers to select the best path when there are two or more different routes to the same destination from different routing protocols. Administrative distance defines the reliability of a routing protocol. Administrative distance is the feature used by routers to select the best path when there are two or more different routes to the same destination from different routing protocols. Administrative distance defines the reliability of a routing protocol.
Question 7
What are two benefits of network automation? (Choose two)
- reduced operational costs
- reduced hardware footprint
- faster changes with more reliable results
- fewer network failures
- increased network security
Correct answer: AC
Question 8
Drag and drop the WLAN components from the left onto the correct descriptions on the right.
Correct answer: To work with this question, an Exam Simulator is required.
Explanation:
The service port can be used management purposes, primarily for out-of-band management.However, AP management traffic is not possible across the service port. In most cases, the service port is used as a "last resort" means of accessing the controller GUI for management purposes. For example, in the case where the system distribution ports on the controller are down or their communication to the wired network is otherwise degraded.A dynamic interface with the Dynamic AP Management option enabled is used as the tunnel source for packets from the controller to the access point and as the destination for CAPWAP packets from the access point to the controller.The virtual interface is used to support mobility management, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) relay, and embedded Layer 3 security such as guest web authentication. It also maintains the DNS gateway host name used by Layer 3 security and mobility managers to verify the source of certificates when Layer 3 web authorization is enabled.Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/wireless/controller/8-5/config-guide/b_cg85/ports_and_interfaces.html The service port can be used management purposes, primarily for out-of-band management.
However, AP management traffic is not possible across the service port. In most cases, the service port is used as a "last resort" means of accessing the controller GUI for management purposes. For example, in the case where the system distribution ports on the controller are down or their communication to the wired network is otherwise degraded.
A dynamic interface with the Dynamic AP Management option enabled is used as the tunnel source for packets from the controller to the access point and as the destination for CAPWAP packets from the access point to the controller.
The virtual interface is used to support mobility management, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) relay, and embedded Layer 3 security such as guest web authentication. It also maintains the DNS gateway host name used by Layer 3 security and mobility managers to verify the source of certificates when Layer 3 web authorization is enabled.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/wireless/controller/8-5/config-guide/b_cg85/ports_and_interfaces.html
Question 9
Drag and drop the threat-mitigation techniques from the left onto the types of threat or attack they mitigate on the right.
Correct answer: To work with this question, an Exam Simulator is required.
Explanation:
Double-Tagging attack: In this attack, the attacking computer generates frames with two 802.1Q tags. The first tag matches the native VLAN of the trunk port (VLAN 10 in this case), and the second matches the VLAN of a host it wants to attack (VLAN 20).When the packet from the attacker reaches Switch A, Switch A only sees the first VLAN 10 and it matches with its native VLAN 10 so this VLAN tag is removed. Switch A forwards the frame out all links with the same native VLAN 10. Switch B receives the frame with an tag of VLAN 20 so it removes this tag and forwards out to the Victim computer.Note: This attack only works if the trunk (between two switches) has the same native VLAN as the attacker.To mitigate this type of attack, you can use VLAN access control lists (VACLs, which applies to all traffic within a VLAN. We can use VACL to drop attacker traffic to specific victims/servers) or implement Private VLANs.ARP attack (like ARP poisoning/spoofing) is a type of attack in which a malicious actor sends falsified ARP messages over a local area network as ARP allows a gratuitous reply from a host even if an ARP request was not received. This results in the linking of an attacker's MAC address with the IP address of a legitimate computer or server on the network. This is an attack based on ARP which is at Layer 2. Dynamic ARP inspection (DAI) is a security feature that validates ARP packets in a network which can be used to mitigate this type of attack. Double-Tagging attack:
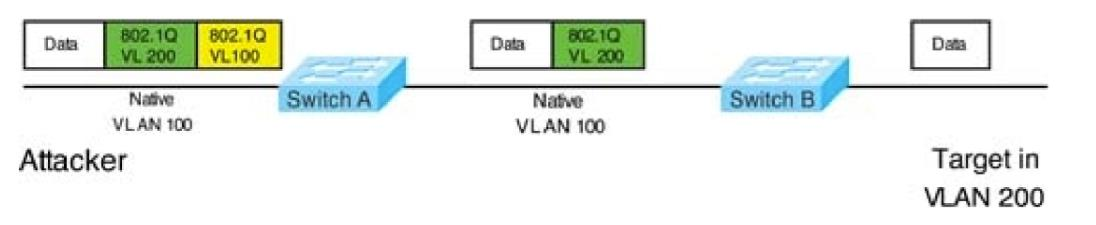
In this attack, the attacking computer generates frames with two 802.1Q tags. The first tag matches the native VLAN of the trunk port (VLAN 10 in this case), and the second matches the VLAN of a host it wants to attack (VLAN 20).
When the packet from the attacker reaches Switch A, Switch A only sees the first VLAN 10 and it matches with its native VLAN 10 so this VLAN tag is removed. Switch A forwards the frame out all links with the same native VLAN 10. Switch B receives the frame with an tag of VLAN 20 so it removes this tag and forwards out to the Victim computer.
Note: This attack only works if the trunk (between two switches) has the same native VLAN as the attacker.
To mitigate this type of attack, you can use VLAN access control lists (VACLs, which applies to all traffic within a VLAN. We can use VACL to drop attacker traffic to specific victims/servers) or implement Private VLANs.
ARP attack (like ARP poisoning/spoofing) is a type of attack in which a malicious actor sends falsified ARP messages over a local area network as ARP allows a gratuitous reply from a host even if an ARP request was not received. This results in the linking of an attacker's MAC address with the IP address of a legitimate computer or server on the network. This is an attack based on ARP which is at Layer 2. Dynamic ARP inspection (DAI) is a security feature that validates ARP packets in a network which can be used to mitigate this type of attack.
Question 10
Drag and drop the functions from the left onto the correct network components on the right.
Correct answer: To work with this question, an Exam Simulator is required.
HOW TO OPEN VCE FILES
Use VCE Exam Simulator to open VCE files

HOW TO OPEN VCEX AND EXAM FILES
Use ProfExam Simulator to open VCEX and EXAM files


ProfExam at a 20% markdown
You have the opportunity to purchase ProfExam at a 20% reduced price
Get Now!



